The construction industry significantly contributes to carbon emissions worldwide. To achieve decarbonisation goals, it is crucial to focus on this sector. Utilising heat pumps in buildings is an effective solution that can make a contribution towards these targets even if they do not solely rely on renewable electricity (although that would be ideal).
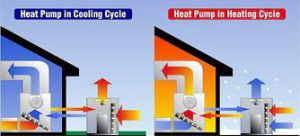
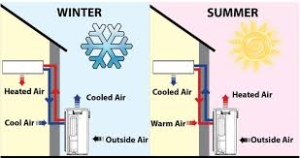
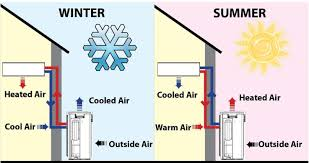
The refrigerant plays a role in the effectiveness of heat pumps. It circulates through a system, absorbing and releasing heat as it moves along. The system functions like an air conditioner by extracting heat from the atmosphere and bringing it indoors to warm up houses or offices. In hot temperatures, the system absorbs heat from either the ground or water source to keep buildings cool. This reduces cooling energy demand and subsequently lowers carbon emissions. To find out more about Air Source Heat Pumps Cheltenham, go to GSM, suppliers of Air Source Heat Pumps Cheltenham.
If all 68 million gas boilers present in households were replaced with heat pumps there would be a 36% reduction in total energy consumption and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions related to building heating. Additionally, assuming that electricity used to power these heat pumps is produced without any fossil fuels, only minimal leakage of gases into the environment would remain – far lower than GHG emissions, from gas boilers.
In addition to the impact on the climate a widespread adoption of heat pumps brings advantages for households. It can help low income families reduce their heating bills by around 2-6%. This makes heat pumps a force for driving change and a crucial element in the broader campaign to achieve net zero and low carbon goals for buildings.