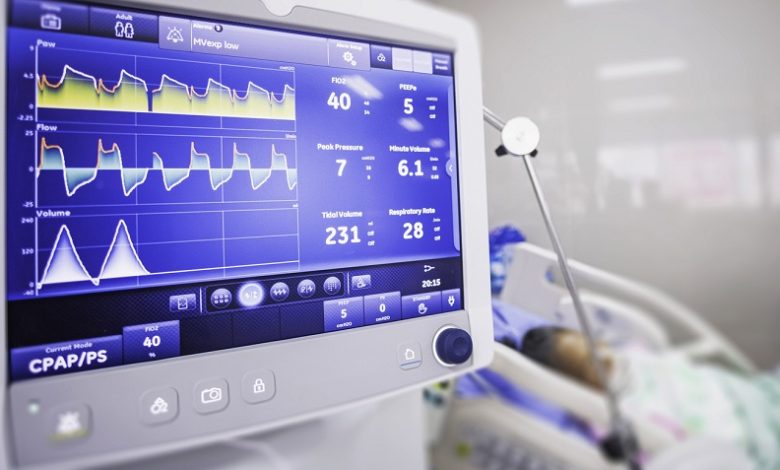
Imagine a technology that can optimize ventilation for patients in a way that ensures their comfort and safety. Enter Pressure Regulated Volume Control (PRVC). This ventilation mode offers a unique approach to respiratory support. In this article, we will delve into the details of PRVC, exploring how it works, its advantages, clinical applications, and more.
Providing adequate ventilation to patients with respiratory insufficiency is paramount in critical care settings. Traditional ventilation modes have their limitations, often failing to address the specific needs of patients. That’s where PRVC comes in, revolutionizing how we deliver respiratory support.
What is Pressure Regulated Volume Control (PRVC)?
PRVC is an advanced ventilation mode that combines the benefits of pressure control and volume control ventilation. It allows clinicians to set a target tidal volume while maintaining a constant pressure throughout the respiratory cycle. By regulating the pressure, PRVC ensures that the desired tidal volume is consistently delivered to the patient.
How Does PRVC Work?
Pressure Control
In PRVC, the ventilator applies constant pressure during the inspiratory phase of the respiratory cycle. This pressure ensures that the desired tidal volume is achieved by adjusting the inspiratory flow rate. By maintaining a stable pressure, PRVC minimizes the risk of barotrauma while optimizing oxygenation.
Volume Control
On the other hand, PRVC also takes into account the patient’s lung compliance and resistance. It adjusts the inspiratory pressure to compensate for changes in compliance and resistance, ensuring that the desired tidal volume is consistently delivered.
Advantages of PRVC
PRVC offers several advantages over traditional ventilation modes. Let’s explore some of the key benefits:
Improved Oxygenation
By maintaining constant pressure and adjusting the inspiratory flow rate, PRVC optimizes oxygenation. It ensures that the desired tidal volume is delivered even in the presence of changes in lung compliance and resistance.
Better Synchronization
PRVC enhances patient-ventilator synchrony by adapting to the patient’s breathing pattern. It provides support when needed and allows the patient to breathe spontaneously during the expiratory phase. This synchronization improves patient comfort and reduces the work of breathing.
Reduced Risk of Barotrauma
With its pressure-regulated approach, PRVC minimizes the risk of barotrauma, a condition characterized by lung damage due to excessive pressure. By maintaining a stable pressure, PRVC ensures patient safety while delivering effective ventilation.
Clinical Applications of PRVC
PRVC has found applications in various clinical scenarios. Let’s explore some of them:
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
PRVC can provide optimal lung protection in patients with ARDS by maintaining a low tidal volume and limiting the peak inspiratory pressure. This protective ventilation strategy helps prevent ventilator-induced lung injury and improves patient outcomes.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
PRVC can be particularly beneficial for patients with COPD. By adapting to the patient’s breathing pattern, PRVC improves patient-ventilator synchrony and reduces the risk of breath stacking, a phenomenon that can worsen air trapping in COPD patients.
Neonatal Ventilation
PRVC is a valuable tool for providing respiratory support to premature infants with underdeveloped lungs in neonatal intensive care units. Its ability to maintain stable pressure and deliver consistent tidal volume makes it a preferred ventilation mode in this population.
PRVC vs. Other Ventilation Modes
PRVC stands out among other ventilation modes due to its unique features. Let’s compare PRVC with some commonly used modes:
Assist-Control Ventilation (ACV)
Unlike ACV, which delivers a set tidal volume regardless of patient effort, PRVC adjusts the inspiratory pressure to maintain the desired tidal volume while allowing for patient-ventilator synchrony.
Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (SIMV)
While SIMV delivers breaths at set intervals, PRVC adapts to the patient’s breathing pattern, providing support when needed. This adaptability improves patient comfort and reduces the risk of patient-ventilator asynchrony.
Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV)
PSV augments patient-initiated breaths, whereas PRVC combines the benefits of pressure control and volume control ventilation. PRVC provides a more comprehensive approach to ventilation, ensuring optimal delivery of tidal volume while maintaining stable pressure.
How to Set Up PRVC on a Ventilator
Setting up PRVC on a ventilator requires attention to specific parameters. Here’s a general guideline:
Initial Settings
- Set the desired tidal volume.
- Choose an appropriate respiratory rate.
- Determine the fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2).
- Establish the positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) level.
Adjusting Parameters
Regularly assess the patient’s lung compliance and resistance to optimize the PRVC settings. Make adjustments based on the patient’s response, ensuring that the desired tidal volume is consistently delivered while maintaining stable pressure.
Limitations and Considerations
Although PRVC offers significant advantages, it’s important to consider certain limitations and factors that may affect its application:
Patient-Related Factors
- Patients’ lung compliance and resistance may change over time, requiring adjustments in PRVC settings.
- Patient-ventilator asynchrony may still occur in certain cases and should be carefully monitored.
Ventilator-Related Factors
- Availability of PRVC may vary depending on the type of ventilator used.
- Proper training and understanding of PRVC are essential for healthcare professionals to utilize this mode effectively.
Conclusion
Pressure Regulated Volume Control (PRVC) is a game-changer in respiratory support. By combining pressure control and volume control ventilation advantages, PRVC ensures consistent tidal volume delivery while maintaining stable pressure. Its benefits include improved oxygenation, better synchronization, and reduced risk of barotrauma. PRVC has diverse applications in various clinical scenarios, such as ARDS, COPD, and neonatal ventilation. While considering its limitations and factors, PRVC remains a valuable tool for optimizing ventilation and improving patient outcomes.