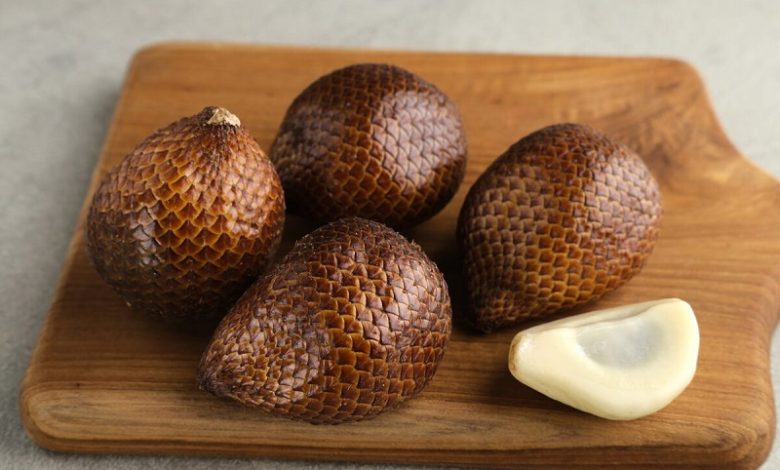
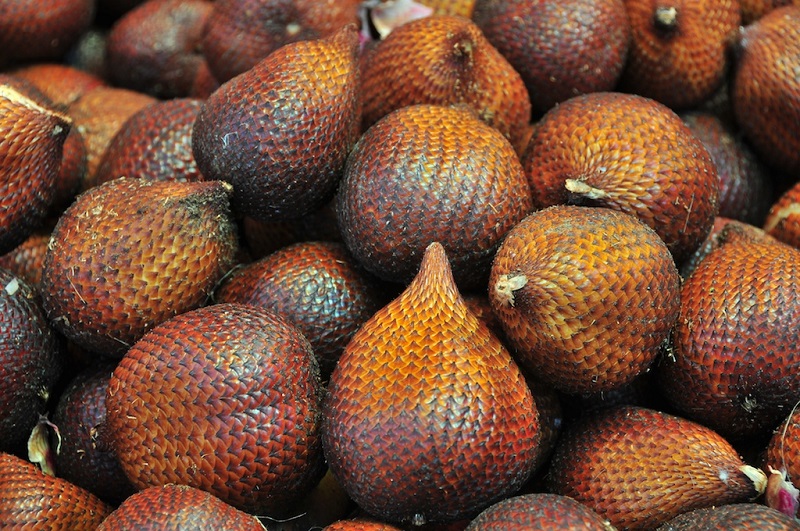
Salacca malacca is the scientific name for an exotic fruit of oriental origin also known as salak, snake fruit, or cayigo. All nicknames are due to the appearance of the peel. It is an abundant fruit in Southeast Asia and some tropical countries.
It is known for its pharmacological and antioxidant properties. It is also very nutritious. It tastes exquisite and is a favorite fruit in Asian food culture.
Origin of salak or snake fruit
The salak is the fruit of a palm that belongs to the Arecaceae family cultivated in Indonesia since 1500. It is a spontaneous plant that, in its natural environment, can bear fruit for 50 years.
Native to Indonesia, the snake fruit has spread throughout Southeast Asia, to countries such as Malaysia, Thailand, and Myanmar. Also in the Philippines, Australia, China, Suriname, and Spain.
On the American continent, it has found an ideal habitat in Ecuador, mainly in the Amazon, in the provinces of Napo, Sucumbíos, and Orellana, as it develops best in tropical climates.
Characteristics of the Salak
- The Salacca malacca is a small palm tree with a short stem, with spiny leaves and fruits that grow at the base of the plant.
- Salak grows in clusters with 15 – 40 fruits and there are several varieties. They are covered in brown skin with small spines and similar to snakeskin.
- The salak Bali variety has a reddish-brown hue and a shell texture that resembles snakeskin. The pulp is white with beige tones and has three lobes that contain the seeds.
- The flavor varies from sour to sweet and the texture is crunchy. It is also astringent when green and as it matures it becomes sweeter.
- The yellow salak has a texture and flavor similar to Bali, but its skin is yellow with golden hues. It has a delicate and smooth pulp, acid taste, and a lot of juice.
Nutritional properties
A study on the nutritional characteristics of salak found interesting amounts of vitamins and minerals in the fruit, as well as a high fiber content per 100 grams of fruit:
- Moisture : 81.29 grams.
- Protein : 0.69 grams.
- Total carbohydrates : 17.11 grams.
- Fiber : 16.55 grams.
- Fat : 0.34 grams.
- Phosphorus : 1169 milligrams / kg.
- Potassium : 1339 milligrams / kg.
- Calcium : 220 milligrams / kg.
- Magnesium : 607 milligrams / kg.
- Iron : 12 milligrams / kg.
- Zinc : 104 milligrams / kg.
- Vitamin C : 400 milligrams / kg.
- Vitamin B2 : 6.32 milligrams / kg.
- Niacin : 240 milligrams / kg.
- Vitamin B1 : 20 milligrams / kg.
Another research shows that salak contains more phytochemicals than other exotic fruits. In addition, sugars give it a sweet taste once it reaches maturity.
In the same study, substances with healing properties are cited: flavonoids, phenols, gallic acid and other antioxidants.
Benefits of salak
The nutrients and phytochemicals contained in salak can alleviate some health problems; moreover, the properties of the fruit are exploited by the food industry.
Antioxidant properties
A diet rich in antioxidants helps fight the action of free radicals . Several laboratory tests have found a good antioxidant capacity in salak pulp, linked to the presence of vitamin C.
Another study highlighted the polyphenol content of salak and its antioxidant power in rats with high cholesterol. A diet supplemented with snake fruit pulp showed a significant reduction in plasma lipids.
Not only the pulp has antioxidant capacity. Research has identified in the skin of the snake fruit a quantity of polyphenols sufficient to increase its antioxidant potential.
It can help control type 2 diabetes
A research team found that small amounts of salak vinegar would be able to lower blood sugar, as well as regenerate damaged pancreatic cells. However, the research was only conducted on mice.
This fruit also has an inhibitory effect on some digestive enzymes. This helps reduce glucose uptake in type 2 diabetic patients. However, further human studies are needed to confirm this effect.
Effect against uric acid
A review article refers to the presence of two active compounds in snake fruit: beta-sitosterol and methyl ester, related to gout relief. However, the methyl ester has shown better results in preventing the formation of uric acid crystals.
Prevention of chronic diseases
Although more human studies are needed, according to an article published in the Journal of Functional Foods , the presence of antioxidants in salak fruit could have an anti-cancer effect. Antioxidants could help prevent heart disease, stroke, and menopausal symptoms .
Other properties
Snake fruit is used in the food industry to isolate the yeast used in bread making. The yeast obtained has a better fermentation capacity than the traditional ones, it allows a good development of the color of the crust and the consistency of the crumb.
Fruit herbal teas can be prepared, for example by combining them with pineapple. The optimal formula for a healthy and effective drink would see the pineapple, salk and logan ratio of 20:20:60.
Gastronomic uses of salak
In the book of Paull and Duarte, some preparations made with the fruit of the snake are described. Ripe salak has a sweet and sour flavor that pleases most palates.
It would be good to eat it raw, but it is generally used to prepare preserves, desserts, jams, juices, syrups and candies. Once dried they are eaten as chips.
In Thailand, a curry mix is prepared with this fruit. Dumplings are made in Malaysia. The texture of the snake fruit makes the cakes delicious and is also recommended for weight loss.